Importance of Routines in Early Childhood
Early childhood routines profoundly impact cognitive and emotional growth, fostering a secure base for learning and engagement․ Consistent routines embed organizational skills,
supporting development;

Early childhood represents a period of remarkable brain development, laying the groundwork for future learning, behavior, and overall well-being․ Within this critical phase, establishing predictable routines isn’t merely about creating order; it’s about building a secure and nurturing environment where children can thrive․ Experts emphasize that learning commences even before birth, with newborns demonstrating an immediate capacity to discern sounds and voices – essentially acting as “little sponges,” absorbing information from their surroundings․
Consistent routines provide a sense of safety and predictability, reducing stress and anxiety in young children․ This secure base allows them to explore, experiment, and engage more fully with their environment․ As highlighted by Joan Lombardi, routines are fundamental to early opportunities and support cognitive development․ The importance of early childhood care and stimulation is consistently underscored, with well-cared-for and stimulated children demonstrating more positive developmental outcomes as they mature․
Understanding this foundational role is crucial for parents, educators, and caregivers alike, as it informs the strategies used to support optimal child development․
What is Early Childhood? Defining the Critical Period
Early childhood is generally defined as the period from birth to eight years old, though its most impactful phase spans from birth to age five; This timeframe is considered a ‘critical period’ due to the unparalleled rate of brain development occurring during these years․ Experts note that children are remarkably receptive to learning from the moment they are in the womb, demonstrating an innate ability to process sensory information and distinguish between sounds․
During this period, neural connections are formed at an astonishing pace, shaping the foundation for cognitive, emotional, and social skills․ This makes early experiences – and the routines that structure those experiences – profoundly influential․ The quality of care and stimulation received during these formative years significantly impacts a child’s future trajectory․
Establishing consistent routines isn’t simply about convenience; it’s about capitalizing on this critical window of opportunity to foster healthy brain development and lay the groundwork for lifelong learning․ It’s a time of immense plasticity, where interventions and positive experiences can have lasting effects․
The Neuroscience of Routine: Brain Development and Predictability
The developing brain thrives on predictability․ Routines provide this crucial element, reducing stress and allowing cognitive resources to be allocated towards learning and exploration rather than constant threat assessment․ When children know what to expect, the amygdala – the brain’s fear center – remains calmer, fostering a sense of safety and security․
This predictability strengthens neural pathways associated with emotional regulation and self-control․ Repeated experiences within a consistent framework reinforce these connections, making them more efficient over time․ Furthermore, routines support the development of the prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions like planning, organization, and impulse control․
Essentially, routines ‘scaffold’ brain development, providing a stable structure upon which more complex skills can be built․ The brain anticipates the sequence of events, freeing up mental energy and enhancing cognitive processing․ This neurological basis underscores why consistent routines are so vital for young children’s optimal development․
Benefits of Routines for Cognitive Development
Routines significantly enhance cognitive development by providing a structured framework for learning․ They support the development of essential organizational skills, enabling children to anticipate events and understand sequences – foundational elements for problem-solving and critical thinking; Knowing what comes next reduces cognitive load, allowing children to focus on mastering new concepts․
Consistent routines also foster memory development․ Repeated experiences strengthen neural connections, making it easier for children to recall information and apply it in different contexts․ This predictability aids in the development of early literacy and numeracy skills, as children begin to recognize patterns and anticipate outcomes․
Moreover, routines create opportunities for embedded learning․ Activities like story time during bedtime or counting during snack time seamlessly integrate educational elements into daily life․ This approach makes learning more engaging and meaningful, promoting deeper understanding and retention․ Ultimately, routines lay a strong cognitive foundation for future academic success․

Routines and Emotional Regulation in Young Children
Routines play a crucial role in fostering emotional regulation in young children․ Predictability reduces anxiety and stress, creating a sense of safety and security․ When children know what to expect, they are less likely to experience emotional outbursts or challenging behaviors stemming from uncertainty․
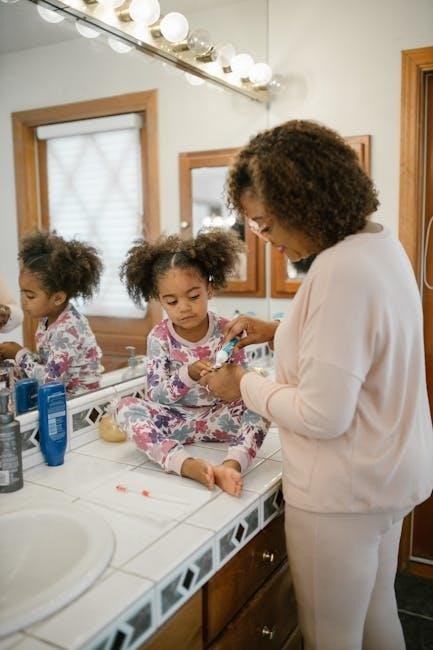
Consistent routines help children develop self-control and coping mechanisms․ Successfully navigating familiar sequences – like getting dressed or brushing teeth – builds confidence and a sense of mastery․ This, in turn, strengthens their ability to manage frustration and regulate their emotions in other situations․
Furthermore, routines provide opportunities for adults to model and teach emotional regulation strategies․ Calmly guiding children through routines, acknowledging their feelings, and offering support fosters a secure attachment and promotes healthy emotional development․ A predictable environment allows children to feel grounded, enabling them to explore their emotions safely and develop resilience․
Social-Emotional Development Supported by Consistent Routines
Consistent routines significantly bolster social-emotional development in young children; Predictable interactions within routines – like shared mealtimes or bedtime stories – create opportunities for positive relationships and emotional bonding with caregivers․ These interactions foster a sense of belonging and security, crucial for healthy social-emotional growth․
Routines also provide a framework for learning social skills․ Children learn to take turns, share, and cooperate during routine activities․ They observe and internalize appropriate social behaviors modeled by adults and peers, enhancing their ability to navigate social situations effectively․

Moreover, successful navigation of routines builds self-confidence and self-esteem․ Mastering daily tasks and expectations contributes to a child’s sense of competence and independence․ This positive self-perception supports their willingness to engage in social interactions and develop healthy relationships, ultimately fostering emotional well-being․
Routines and Language Development: Creating Opportunities for Communication
Daily routines are fertile ground for language development in early childhood․ Repeated experiences within routines – such as dressing, bathing, or meal preparation – provide predictable contexts for communication․ Caregivers can narrate actions, label objects, and ask simple questions, expanding a child’s vocabulary and comprehension․
These consistent interactions expose children to a rich linguistic environment, reinforcing language patterns and grammatical structures․ Routines encourage reciprocal communication; children begin to anticipate what comes next and actively participate by vocalizing, gesturing, or attempting to verbalize their needs and desires․

Furthermore, routines offer opportunities to introduce new concepts and vocabulary related to specific activities․ For instance, during cooking, caregivers can discuss ingredients, measurements, and cooking processes․ This contextualized learning enhances language acquisition and prepares children for more complex communication skills, fostering overall cognitive growth․
The Role of Routines in Fostering Independence
Consistent routines play a crucial role in nurturing independence in young children; Predictability empowers them to anticipate expectations and gradually take ownership of tasks within those routines․ When children know what comes next, they experience a sense of control and competence, boosting their self-confidence․
Routines provide structured opportunities for children to practice self-help skills, such as dressing themselves, tidying up toys, or washing their hands․ Initially, caregivers offer support and guidance, but as children become more familiar with the routine, they can perform increasingly more steps independently․
This gradual progression fosters a sense of mastery and encourages children to attempt new challenges․ By breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable steps within a routine, caregivers facilitate success and build a child’s belief in their abilities․ Ultimately, well-established routines lay the foundation for self-reliance and a proactive approach to learning and problem-solving․
Routines and Literacy/Numeracy Skills
Daily routines are fertile ground for embedding early literacy and numeracy skills․ Storytime before nap, for instance, cultivates a love of reading and expands vocabulary․ Counting during snack time or sorting toys by color introduces foundational math concepts in a natural, engaging way․
The repetitive nature of routines provides ample opportunities for children to practice and reinforce these skills․ Songs, rhymes, and fingerplays incorporated into routines enhance phonological awareness – a crucial precursor to reading․ Similarly, routines involving shapes, sizes, and patterns build early mathematical thinking․

Furthermore, routines create a context for meaningful communication․ Children learn to ask questions, make predictions, and retell events, strengthening their language skills․ By intentionally integrating literacy and numeracy into everyday routines, caregivers can seamlessly support children’s cognitive development and prepare them for future academic success․
Impact of COVID-19 Lockdowns on Routine and Child Development
The COVID-19 lockdowns significantly disrupted established routines for young children, raising concerns about long-term developmental effects․ Clinicians and educators in the UK, and globally, have observed setbacks in speech and language development, likely linked to reduced social interaction and altered daily structures․
The absence of predictable routines created instability and anxiety for many children, impacting their emotional regulation and social-emotional wellbeing․ Limited access to early childhood education settings further exacerbated these challenges, depriving children of crucial opportunities for learning and development․
Disrupted routines also affected the consistent reinforcement of early literacy and numeracy skills․ The lack of structured activities and interactions hindered cognitive growth․ Addressing these impacts requires targeted interventions and a renewed focus on re-establishing predictable, nurturing routines to support children’s recovery and future success․
Addressing the Effects of Disrupted Routines
Mitigating the developmental impacts of disrupted routines requires a multi-faceted approach, prioritizing re-establishment of predictability and security for young children․ Parents and educators should collaboratively create consistent, age-appropriate daily schedules, incorporating familiar activities and transitions․
Focusing on strengthening attachment relationships is crucial, providing children with a secure base from which to explore and learn․ Targeted interventions, such as speech and language therapy, can address specific developmental delays exacerbated by the pandemic․
Creating opportunities for social interaction and play is essential for fostering social-emotional development․ Prioritizing play-based learning and embedding learning opportunities within routines can enhance cognitive growth․ Acknowledging and validating children’s feelings about the disruptions can also aid in their emotional recovery, fostering resilience and a positive outlook․
Creating Effective Routines: Key Principles
Establishing effective routines centers on predictability, consistency, and age-appropriateness․ Routines should be visually supported, utilizing picture schedules to aid comprehension, particularly for younger children․ Transitions between activities must be clear and gentle, minimizing anxiety and promoting cooperation․
Flexibility is paramount; routines shouldn’t be rigid but adaptable to individual needs and unforeseen circumstances․ Incorporating child choice within routines fosters a sense of autonomy and engagement․ Routines should also be intentionally designed to support key developmental areas – cognitive, social-emotional, and language․
Regular review and adjustment are vital, ensuring routines continue to meet the evolving needs of the child․ Parental involvement and consistency across settings (home and childcare) amplify the benefits․ Remember routines aren’t about control, but about providing a secure and supportive framework for learning and growth․
Age-Appropriate Routines: Adapting to Developmental Stages
Routines must evolve alongside a child’s developing capabilities․ Infant routines center on feeding, sleeping, and comforting, prioritizing responsiveness to cues․ Toddler routines introduce simple self-care tasks, like washing hands, fostering independence․ Preschool routines expand to include structured learning activities and social interactions․
As children mature, routines can incorporate more complex tasks and responsibilities․ The length and complexity of routines should be adjusted to match attention spans and cognitive abilities․ Visual supports remain valuable, but can gradually transition to verbal cues as language skills develop․

Understanding developmental milestones is crucial for creating routines that are both supportive and challenging․ Routines should provide opportunities for skill-building, while avoiding frustration․ Flexibility is key; adapting routines to accommodate individual temperaments and learning styles maximizes their effectiveness․
Examples of Daily Routines in Early Childhood Settings

A typical early childhood setting incorporates several key routines․ Morning arrival routines establish a sense of security and belonging, including greeting rituals and designated space for belongings․ Circle time routines foster social interaction, language development, and pre-literacy skills through songs, stories, and discussions․
Mealtime routines promote healthy eating habits and social skills, emphasizing polite conversation and self-help skills․ Naptime routines provide a calming transition to rest, utilizing quiet activities and consistent procedures․ Outdoor play routines encourage physical activity and exploration, with clear expectations for safety and behavior․
Departure routines signal the end of the day, including packing belongings, saying goodbyes, and preparing for the transition home․ These routines, when consistently implemented, create a predictable and supportive environment for young children’s growth and learning․
The Importance of Flexibility Within Routines
While routines provide essential predictability, rigid adherence can be counterproductive․ Flexibility within routines acknowledges that children’s needs and circumstances vary daily․ Unexpected events, like illness or changes in weather, necessitate adjustments to the schedule․ A skilled educator anticipates these possibilities and prepares alternative activities․
Allowing children some choice within routines – selecting a book during story time or choosing a building block – fosters a sense of autonomy and engagement․ Responding sensitively to a child’s emotional state, even if it means temporarily deviating from the plan, demonstrates empathy and builds trust․
Flexibility doesn’t negate the benefits of routines; rather, it enhances them․ It teaches children adaptability, problem-solving skills, and resilience – crucial life skills developed within a supportive and understanding environment․ A balanced approach ensures routines remain beneficial without becoming restrictive․
Routines and Reducing Behavioral Challenges
Predictable routines significantly contribute to minimizing behavioral issues in young children․ When children understand what to expect, anxiety and uncertainty decrease, leading to fewer outbursts and challenging behaviors․ Clear expectations embedded within routines provide a framework for appropriate conduct․
Routines offer opportunities to proactively teach and reinforce positive behaviors․ For example, a consistent cleanup routine can transform a potentially frustrating task into a cooperative activity; Visual schedules and verbal cues further support understanding and compliance․
Disruptions to routines can often trigger behavioral challenges․ Recognizing this connection allows caregivers to anticipate potential difficulties and offer extra support during transitions․ Consistent routines create a sense of safety and security, fostering emotional regulation and reducing the likelihood of disruptive behavior․ A well-structured environment promotes self-control and positive social interactions․
Parental Involvement and Routine Consistency
Consistent routines are most effective when parents actively participate and reinforce them, creating a unified approach between home and early childhood settings․ Parental involvement demonstrates the value placed on structure and predictability, strengthening the child’s sense of security․
Open communication between parents and educators is crucial for aligning routines and addressing any challenges․ Sharing information about daily schedules, expectations, and strategies ensures consistency across environments․ This collaborative effort maximizes the benefits of routines for the child’s development․
Parents can support routine consistency by establishing similar patterns at home, even on weekends․ Modeling predictable behaviors and providing clear explanations helps children internalize the importance of structure․ Active participation fosters a strong parent-child bond and reinforces positive behavioral patterns, ultimately contributing to a child’s overall well-being․
Resources and Further Information (PDF Focus)
Numerous resources in PDF format delve into the importance of routines in early childhood․ The Early Opportunities Initiative, spearheaded by Joan Lombardi, offers valuable insights and research findings accessible through downloadable reports and guides․
Stanford University’s Center for Early Childhood provides PDF documents detailing best practices for establishing effective routines, focusing on cognitive and social-emotional development․ These resources emphasize the link between predictability and a child’s ability to thrive․
Organizations like the National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC) frequently publish PDF-based position statements and articles on routine-based care․ Searching for “early childhood routines PDF” yields a wealth of information from various educational institutions and governmental agencies․ These PDFs often include practical tips for parents and educators, alongside research-backed evidence supporting the benefits of consistent routines for young learners․